Use this 2x2 matrix for GenAI risk decisions
Risk strategies, agentic workflows, and more...
Imagine a GenAI-powered content generator is launched that produces witty marketing copy for a major brand. Until one day, when a seemingly harmless joke sparks an unexpected backlash online, forcing the company into full crisis mode.
Did the company err in leveraging GenAI, or merely use it in the wrong way? Today, we synthesize our research on the risks behind different internal and external facing use cases. The result -- a simple framework for avoiding situations like the above.
But first…
5 things to know
📰Quote: “Smart early movers in sectors adopting gen AI have certainly captured some of this value in the short term. But relatively soon all surviving companies in those sectors will have applied gen AI, and it won’t be a source of competitive advantage for any one of them, even where its impact on business and business practices will probably be profound. In fact, it will be more likely to remove a competitive advantage than to confer one.
But here’s a silver lining: If you already have a competitive advantage that rivals cannot replicate using AI, the technology may serve to amplify the value you derive from that advantage.” [HBR]
🎤GenAI Prompt: “What recent trends in consumer preferences are most impactful to [your company]?” Give it a try.
▶️Video: Revolutionizing E-Commerce: AI’s Impact on CX | Amazon Head of Product
🎓Learning: GenAI in Action: Impact and Possibilities [USF]. Free online course offered through March 24, 2025
📅Event: AI Explained: AI Observability and Security for Agentic Workflows. Thursday March 20, 2025 | 10:00AM PT / 1:00PM ET
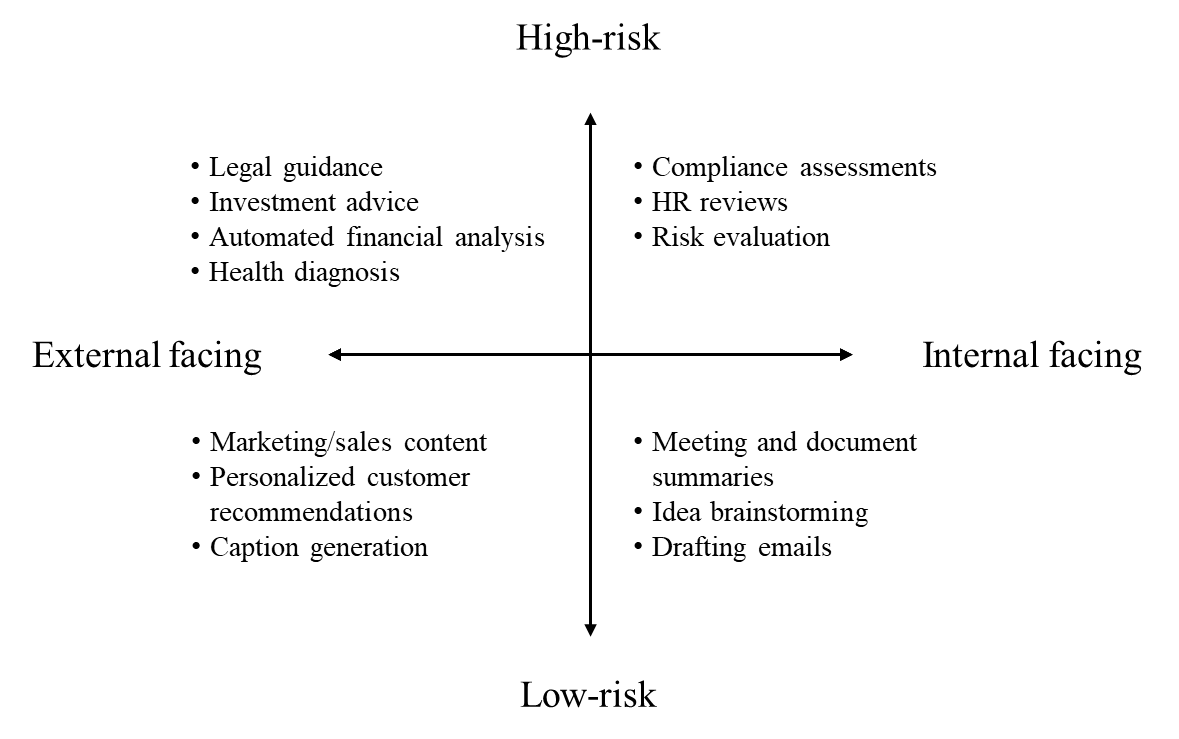
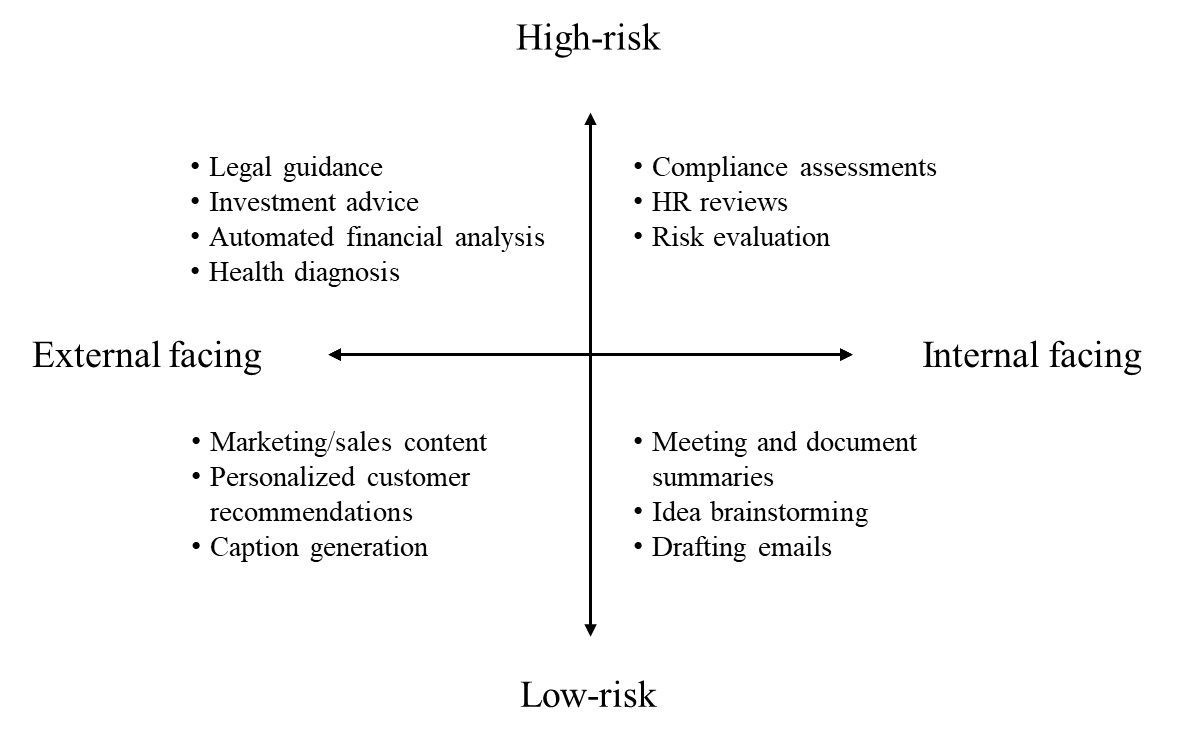
GenAI Use Case Risk Framework
Based on our GenAI use case research over the past few months, we propose the simple 2x2 matrix below for managing the risks of different use cases.
Dimension 1 | Audience: Who the output is intended for
Customer-facing: External users, clients, or the general public
Internal: Employees, internal stakeholders, or business processes
Dimension 2 | Risk Profile: The potential impact of incorrect, biased, or misleading outputs
High-risk: Errors could result in significant harm (e.g., legal, financial, reputational damage)
Low-risk: Errors are manageable or have minimal consequences
Expanded Matrix with Examples
Here’s a 2x2 matrix showing illustrative use cases with associated risk strategies further below. While some key risk strategies could be useful to all quadrants, their need is often higher for certain uses than others. For example, external-facing + high-risk applications would require much more oversight and approval compared to internal + low-risk uses.
So which quadrant does your current project fall in? Use the checklist below to identify potential risk mitigation techniques relevant for each quadrant:
1. External-Facing + High-Risk — Key Risk Strategies:
✅ Human-in-the-loop systems: Ensure outputs are reviewed by qualified professionals before reaching end users.
✅ Explainability & transparency: Use AI ‘thinking’ models that provide clear reasoning for their outputs, especially in regulated industries.
✅ Robust testing and validation: Simulate real-world use cases extensively before deployment.
✅ Audit trails: Maintain detailed logs of model outcomes to enable traceability and accountability.
✅ Fail-safe mechanisms: Design systems that fall back to human handling or low-risk outputs when confidence levels are low.
✅ Scenario planning: Develop contingency plans for worst-case outcomes to ensure rapid response to unexpected outputs.
2. External-Facing + Low-Risk — Key Risk Strategies:
✅ Tone and style guardrails: Use prompt engineering pretext or content filters to ensure outputs align with brand voice.
✅ Feedback loops: Sample user feedback to refine model performance over time.
3. Internal-Facing + High-Risk — Key Risk Strategies:
✅ Access controls: Implement role-based permissions to restrict sensitive data from other users.
✅ Data limits: Limit the model's exposure to only necessary data. Avoid feeding proprietary, confidential, or personally identifiable information (PII) into model training data.
✅ Bias detection: Regularly test for biases that could influence decision-making.
4. Internal-Facing + Low-Risk — Key Risk Strategies:
✅ Encourage sharing: Foster a culture where teams feel safe exploring creative uses of GenAI - and share their lessons learned (good or bad).
✅ Knowledge sharing platforms: Centralize approved tool lists, prompt best practices, and hallucination examples to inform & educate employees about the risks of GenAI tools.
Adventure on.